You have likely recently bought new earphones or speakers.
You are now searching for the correct audio port connections for them on your computer. While they can be connected directly to a monitor, having the inbuilt ones on the motherboard is the best solution.
There are various sorts of audio port , and contemporary circuit boards can contain six or more of them. This, however, is dependent on the model, therefore you may find less on yours. Similarly, most laptop motherboards have only one audio port that may serve as input as well as output.
Because different musical instruments require different connections, it's critical that you understand these audio port. This page will teach you about the audio port located on a motherboard.
It will also explain the position and color of each port.
What is a computer audio port?
The motherboard of a machine has an audio port. This port is used to connect audio devices like speakers, microphones, and home theater systems. The audio port is only functional when a device is connected through an electrical connection or cable. Audio port are required when using Bluetooth technology.
The audio port of a desktop computer are located on the front and back sides of the CPU. However, depending on the manufacturer, the audio port will be situated on either the left or right side of the keypad. There are several techniques to determine the motherboard type on the machine you are using.

A desktop computer's motherboard audio port
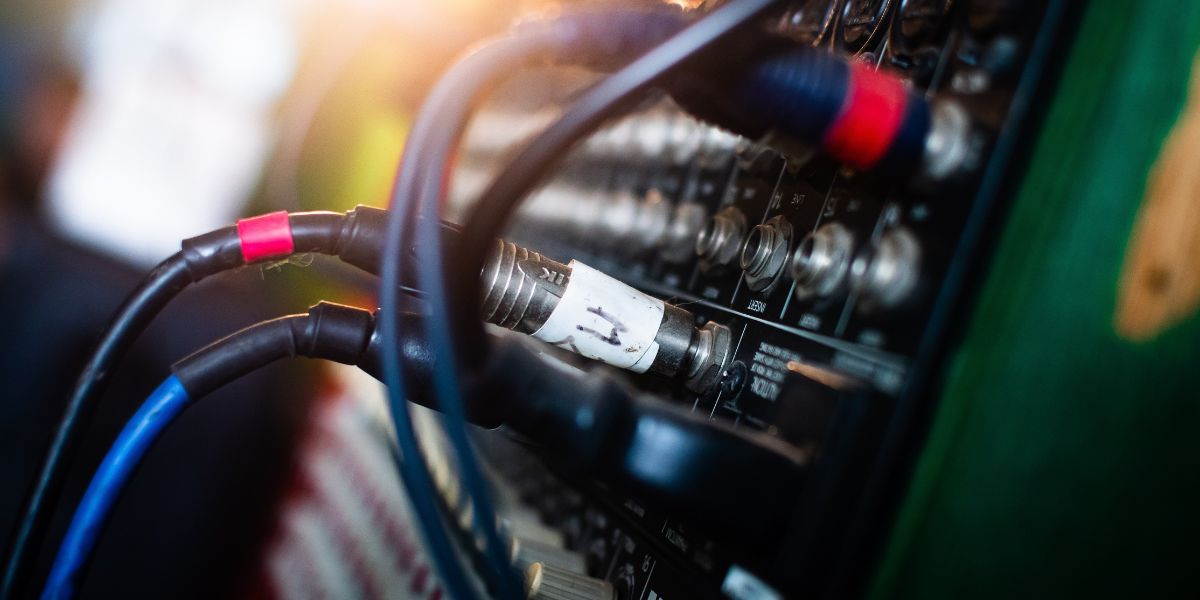
The desktop computer's CPU will have two 3.5 mm jack connectors on the front. One is for receiving audio signals (for speakers), while the other is for providing audio input (microphone).
As a result, both of these audio port are only used for basic functions. However, the audio port parts are colored differently on the CPU's backside. The hues are used to determine the functionality and compatibility of the device.
If you put a microphone in a speaker port, for example, the recording device will not operate. This is due to a signal-passing fault between the devices.
What Are the Various Audio Port on a Motherboard?
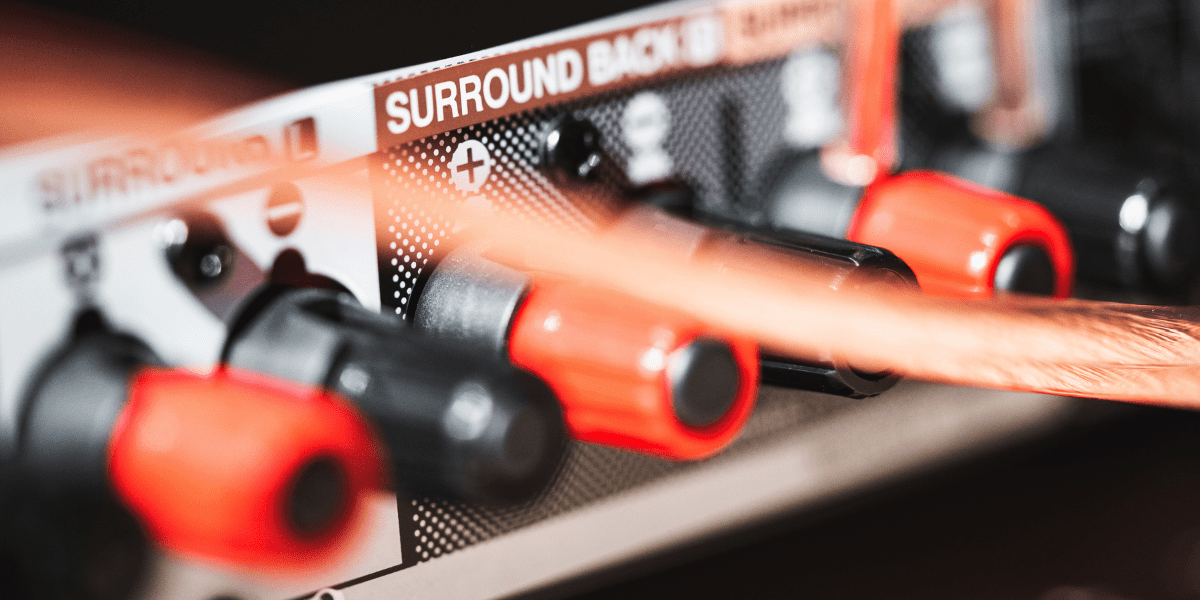
On a computer or motherboard, there are three main audio port: Green, and Pink, and Blue. The green audio port is the primary one here. It can be used to listen to music and other audio port through headphones or speakers. The Pink port is used for recording sounds with a microphone.
The Blue audio port is for connecting additional audio equipment such as home theaters, subwoofers, etc.
There are two audio port on the front of the CPU. The first is for the speaker, while the second is for a microphone or receiver. If you would like to use both of these functionalities simultaneously, you must install a 3.5 mm audio port split.
If you cannot locate the required pins on the computer's motherboard, you can purchase an additional audio port.
Colors of Audio Port and Their Functions
In essence, an audio port connects and communicates any audio equipment with a computer. Although the quantity varies by motherboard, most recent ones follow the PC System Architecture Guide and have five or six ports.
The chart below contains all the information about the audio port on a computer's motherboard. Let's take a look at the details of each port.
|
Audio Port Color |
Compatible Devices |
Audio cable size |
Functionality |
|
Green |
Headphones, earphones, and so on |
3.5 or 6.35 mm |
Listening to music or other audio |
|
Pink |
Headphones, Microphones,or Earphones with Mic |
3.5 mm |
To record the desired audio |
|
Blue |
Home-Theater, Amplifier, Speaker, and so on |
3.5 mm |
To listen to music or audio |
|
Orange |
Subwoofer, Woofer, and Speaker |
3.5 mm |
Organize the audio signals |
|
Black |
Speaker, Subwoofer |
3.5 mm |
To listen to side audio |
|
Silver |
Speaker |
3.5 mm |
particularly |

What Are Different Kinds of Audio Port on a Motherboard?
The audio port is divided into two categories: input and output, just like other computer connectors. Selecting the proper port is important. Neglecting to connect audio devices to the correct audio port can cause problems. These issues include the speaker not working or the computer not recognizing the microphone.
This does not apply to motherboards, mostly laptops. These motherboards have only one specialized audio port. This audio port can work as both ports. When you connect a peripheral, a required driver is downloaded and installed and functions properly.
The majority of motherboard manufacturers utilize standard colors to differentiate input and output ports. Nonetheless, some versions do not use this and instead have only black ones. As a result, icons or labels are the most effective approach for recognizing the interface.
Below is everything you should know about the different types of motherboard audio port, along with their colors and labels.
Microphone port
Microphone-In, sometimes known as Mic-in, is a specialized audio input port for plugging mics. This connector is found on practically every computer motherboard and is easily identified by its pink hue. A 3.5 mm audio jack is needed to connect a microphone to a computer's motherboard. This jack is usually included with the audio device.
Mic-In ports are typically identified with a mic symbol or, in some cases, just MIC. As a result, even if yours lacks this audio port, you ought to be able to recognize it without difficulty.
Furthermore, the pink port is unlikely to be found on the motherboard of your laptop. It instead has a single audio port that accepts both the input (microphone) and outputs (headphone/speaker).
Line-Out
The Line-Out is an output connection. It is also known as the Headphone-Out or Audio-Out.
This connection sends audio from a computer to speakers and headphones. It is typically identified by its green hue as well as a headphone or outward sound wave indicator. It may also be called "AUX" on some motherboards.
This connection is ideal for a 2.0-channel system. It allows you to connect any stereo equipment, such as headphones or speakers. All that's required is a 3.5 mm audio wire for connecting these audio peripherals.
Surprisingly, a few motherboards provide a 6.35 mm connector, which allows additional power to be delivered to the headphones. As a result, a 6.35 mm audio cable has reduced resistance and inductance to accommodate high-end audio equipment.
Line-In
The Line-In port is another important audio port found on most motherboards. This is the one you need.
It is for obtaining audio inputs from third-party audio equipment.
You can use it for recording, playing, and adjusting sound.
You can connect any audio peripheral here. Examples include amplifiers, CD and DVD players, MIDI instruments, etc. In fact, connecting in a microphone will make everything operate flawlessly. However, we recommend connecting this device to the mentioned above Mic-In port because the sound quality is much superior.
The Line-In connection is a pale blue in hue, and an incoming sound indicator appears beneath it. Notebook motherboards do not have a connector. To link the input audio equipment, you must use a conventional audio port.
CS-Out
CS-Out is an audio port output found on high-end motherboards. It allows users to connect surround sound systems. They're orange or lime in color and can be identified by the label "c/sub" or a speaker symbol.
This is the specific connection for connecting the subwoofer, middle/front speaker, or bar to your TV or PC. As a result, these gadgets add more bass to the audio system and are ideal for music aficionados.
Coaxial-Out
Another digital communication audio port on a computer's motherboard is coaxial-Out. The S/PDIF-Out port and the TOSLink port have the same function. The only difference is that the TOSLink port requires a copper or RCA wire to connect to your speakers.
One advantage of adopting Co-axial Out is the fact that it can transmit both audio and digital communications. Furthermore, it has a larger frequency (up to 24-bit/192kHz) compared to the optical connection (up to 96kHz). As a result, Co-axial-Out is the greatest option for linking home theatre systems, digital participants, and headphones..
SS-Out
The computer's motherboard has another audio port called the Side Speakers-Out (SS-Out). It is used to connect to a multichannel sound system. In reality, the presence of such an interface enables the configuration of a 7.1 audio channel system.
Furthermore, SS-Out might be white, silver, or grey in color. If your motherboard lacks color in the audio connectors, look for a label that says "side" and a speaker icon.
RS-Out
The speakers behind you or the rear of the center speakers have a sound output connection. It is called Rear Speaker-Out (RS-Out). This, like the CS-Out, can be used to link surround sound systems.
Furthermore, as with other audio port, identifying the port is simple. All you need to do is look for the black port. However, in motherboards that fail to conform to color standards, look for the term "rear" followed by a speaker sign.























Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.